Deena Engel the Life Cycle of a Software Based Piece of Art
If you take been working as a software professional in the manufacture for a day or a lifetime, then you probably know that the Software Development Life Cycle is part of the daily rituals.
Assuming that you lot don't know anything about SDLC or software development life wheel, this article will fill up yous in on everything you need to get started. We talk about SDLC in general; what it is, how information technology works, what are the phases that it goes through. In addition, we also look at a few software development lifecycle models that help to refine the overall workflow.
What is the Software Development Life Cycle?
Source
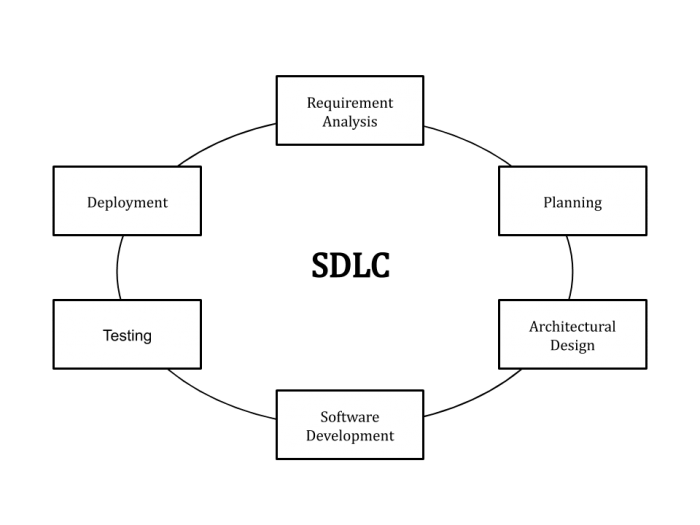
The Software Development Life cycle or SDLC is a thorough procedure to manufacture software that systematically ensures that the quality and the correctness of the software is according to the standards set by the company and the industry.
This life bike aims to ensure that the software's that are being manufactured in the industry are properly falling under the expectation bracket of the customer. One thing it ensures is that the evolution process of the software stays inside the already agreed upon cost and time frame.
The software evolution life bicycle is a compilation of ideas and plans that explain the whole process of planning, building, maintaining software from initiation to completion. And it's not a stagnant procedure either.
In every step of the way, some various processes and deliverables demand to be worked on, to make sure that the next phase of the lifecycle goes smoothly.
Why use SDLC?
The following are a few of the reasons why we SDLC is of import to produce software.
- Information technology offers a ground for projection planning, scheduling, and estimating
- It is a machinery for project tracking and command
- Increased and raise development speed
- Helps you to decrease project take chances and project management programme overhead
- Provides a framework for a standard set of activities and deliverables
- Increases visibility of projection planning to all involved stakeholders of the evolution procedure
- Improved customer relations
What are the Phases included in the Software Development Lifecycle?
Source
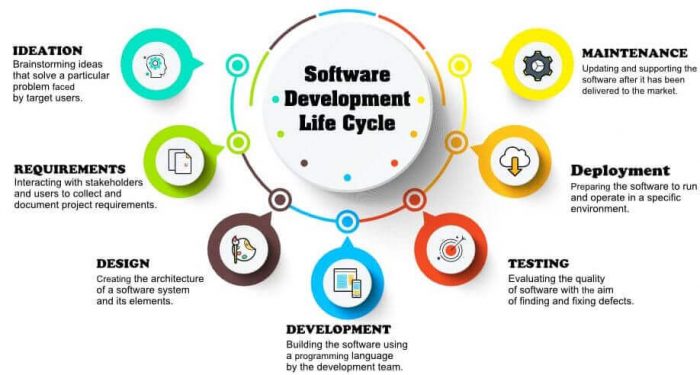
The whole lifecycle is divided into the following stages. They are:
- Requirement collection and analysis
- Design
- Testing
- Maintenance
- Feasibility study
- Coding
- Installation/ Deployment
Allow'south dive into the details of these phases and discover out how the software evolution lifecycle works.
1. Requirements Collections and Analysis

This is the get-go phase of the Software evolution life bike which is executed by the most senior members of the evolution team. This execution is based on the inputs submitted by all of the domain experts and stakeholders continued to the industry.
Ane other important thing that is performed in this stage is the planning for the recognition of whatsoever potential risks and scope creeps, and the quality assurance requirements for the software in question.
This phase is important also because information technology makes the following entities connected to the project, quite clear. They are:
- Project Scope
- Anticipated Opportunities
- Predictable Issues
- Anticipated Directives
Acquire the complete procedure of projection scope, here:
What is Project Management, Your Ultimate Guide on learning the Art
2. Feasibility Study

Once the initial stage in over where we wait over the requirements and how the software is going to be planned, we move on to the side by side step where all of the software needs and requirements are put onto paper and properly documented.
This document that is compiled in this step is done so with the help of the Software Requirement Specification certificate. It is known as the SRS document. This certificate includes every information that is to know about the development procedure and how everything is going to be designed and developed within the projection evolution lifecycle.
Mainly at that place are v different feasibility checks that every project goes through.
- Economical: Tin can this projection be completed on the budget that the whole upper management and the stakeholders signed off on?
- Schedule: Decide that the project can exist completed within the given schedule or non
- Legal: Tin can this project laissez passer the cyber police force requirements and other regulatory compliances?
- Technical: Need to check whether the current computer system can support the software
- Operation feasibility: Tin we create operations that are expected by the customer?
Read this blog:
Your Become-To Guide to Creating 7 Important Project Documents
3. Pattern

In the next stage of the software evolution life bike, all of the software design and system documents are created on the specifications and requirements provided in the requirement specification certificate.
What this does is that it enables the team to easily ascertain every nook and cranny of the system architecture.
Traditionally, there are ii different types of blueprint documents that are created in this stage of the software evolution life cycle. They are:
High-Level Design (HLD)
- Brief description and name of each module
- Interface relationship and dependencies betwixt modules
- Complete architecture diagrams forth with technology details
- An outline of the functionality of every module
- Database tables identified along with their primal elements
Depression-Level Design (LLD)
- Functional logic of the modules
- Complete detail of the interface
- Listing of error messages
- Database tables, which include type and size
- Addresses all types of dependency problems
- Complete input and outputs for every module
You might like these design tools:
12 Best Tools for Web and Graphic Designer
4. Coding

One time the critical blueprint phase is complete, the team members now direct their focus to one of the about important stages of the software development life cycle and that is coding.
In this phase, all of the developers curl their sleeves upwards and bunker own to code the unabridged organisation using the pre-selected programming language by the planning team.
The job allocation is performed in this stage which lets all of the team members and the developers know what their goals and milestones are regarding this project. This is basically the longest phase of the SDLC.
v. Testing

When the coding is complete and the software has been completed, it is passed over to the realm of testing. This is where the testers test each nook and cranny of the software until they detect issues and errors that are hindering a seamless execution of the software.
This testing is performed, to verify that the entire awarding is working without whatsoever hiccups according to the requirements provided to the team past the customer.
In this stage of the SDLC, the testing team finds all of the issues and errors that are putting obstacles in seamless execution of the software and when they discover them, these errors or issues are communicated to the developers.
These developers set these problems and transport the software back to the tester to run a re-exam. This procedure goes dorsum and forth until finally, the software is gratuitous of any issues that hinder its successful execution according to the criteria set past the customer.
Cheque this out:
Top 5 Resources for QA Functioning Analysis
half dozen. Installation
Once the coding and testing of the software have been completed by the respective teams and departments, nosotros move onto the final deployment procedure. The software in this deployment pace is complimentary of any bugs or issues and is finally released, based on the valuable feedback the team receives from the project director.
7. Maintenance
Once the system has been successfully installed or deployed according to the feedback given past the project manager of the whole shebang, the customers start using the software that has been advisedly and expertly crafted by the team members.
When that happens, the following three activities follow arrange. They are as follows:
- Problems fixing – bugs are reported because of some scenarios which are not tested at all
- Enhancement – Adding some new features into the existing software
- Upgrade – Upgrading the awarding to the newer versions of the Software
What Are the Most Popular Models of the Software Development Life Bike?
The post-obit models are the ones that brand up the whole SDLC. They are:
1. Waterfall Model
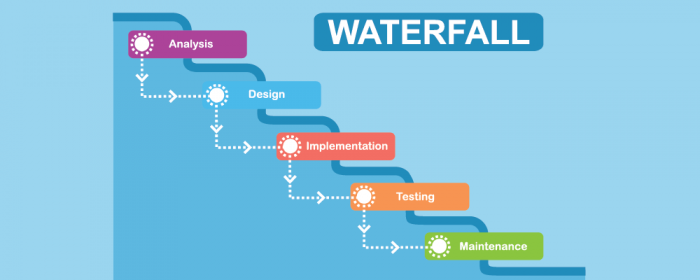
One of the almost important models of the software development life bicycle that is widely accepted across the board is the waterfall model. In this model, the whole bigger chunk of the software evolution process is broken down into tiny phases that the team needs to reach.
In this model, the outcome of the previous phase acts every bit an input for the side by side stage in the roster. 1 other thing to remember is that the waterfall model is very intensive when it comes to documentation. This means that the team has to document every phase as information technology comes forth.
2. V-Model
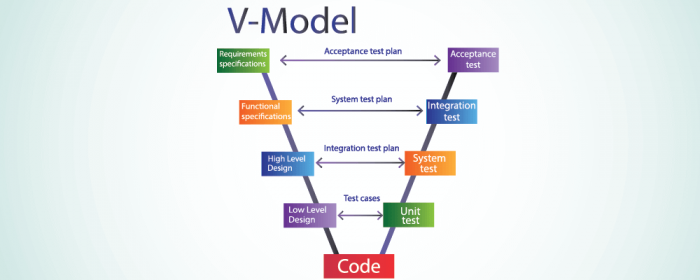
The side by side important model in the software development life wheel is the V-model. In this model, the phases are planned in parallel. This means that all the verifications that are needed and the validations that are necessary for the project are conducted on either the contrary side.
three. Agile Model
The Agile methodology is not only of import but also comes with numerous benefits when it comes to software evolution or even when it comes to the project direction paradigm every bit a whole. This methodology is a vital procedure that enables the interaction of two especially important phases of the SDLC process, which are testing and development.
In the Agile form of activeness, the whole big chunk of the project evolution process is divided into smaller builds that the team members can perform. These builds are performed in small iterations that are chosen sprints. These sprints tin last from ane to iii weeks depending on the size of the team and the development process.
4. Screw Model
The Spiral model of the software development life cycle is a risk-driven 1. This helps all the squad members to adopt 1 or more than process models included in the software evolution life cycle's arsenal like the waterfall, Active or V-model, etc.
This strategy enables the team members to use all of the best features of every one of those models and use them to their reward in the process of software development.
4 Phases of the Projection Management Life Cycle
There are four unlike phases in which the whole project management life cycle is completed. They are:
- Initiation
- Planning
- Execution
- Closure
Let's have a look at all of them in detail and detect out how they contribute to the overall software project development life cycle.
one. Initiation
One thing that you have to always practise regardless of the product that you are trying to develop is to make sure that you take identified a business need or a problem that needs to be solved using your product.
During this phase, you need to figure out a specific objective for your project and as well do an all-encompassing feasibility study on whether or not yous should be spending your money on this projection or maybe you lot should try something else.
2. Planning
The next stride comes afterward your project is approved past the right people or the right stakeholders for the project. And when they have done that, y'all need to plan out the whole project development process from scratch or with some help from any previous projects.
During this phase, you telescopic out the budget, the squad, and also a schedule for your project and so that everything tin be done according to the plan that yous will create for the projection and nothing gets delayed.
3. Execution
Next on the listing is Execution. In this step, the project development process is worked on and all of the tasks and processes related to the project are performed by the relevant people.
All of the plans and schedules that you lot set for the projection development procedure are monitored here and you get the finished product from your project development team.
If you think that you demand projection management software that will help you go on rails of all of those tasks and processes, then you should endeavour out nTask.
iv. Closure
The final pace in this process is Closure. In this stage, y'all need to close down the project development process, clear your ante and proceed your software under observation.
This observation helps you to make sure that the software build is stable and complete, and you have a finished production at hand. In this phase, you too get to know what worked for this project and what didn't, which will assistance you to develop more than stable builds like this in the hereafter.
Conclusion
Based on everything we have talked about the software development lifecycle, some of the cardinal highlights could be summed upwardly as appended below. Behave in listen that SDLC is an ever-evolving miracle due to changing technology and industry needs. Feel free to improvise every bit a project manager – or a program managing director for that matter.
- The SDLC is a systematic process for building software that ensures the quality and correctness of the software congenital
- SDLC process provides a framework for a standard set of activities and deliverables
- The senior team members bear the requirement analysis phase
- In the Blueprint phase, the organisation and software design documents are prepared as per the requirement specification document
- Testing is the next phase which is conducted to verify that the entire awarding works according to the client requirement.
- Issues fixing, upgrade, and engagement actions covered in the maintenance face
- SDLC consists of a detailed plan which explains how to plan, build, and maintain specific software
- The full class SDLC is Software Development Lifecycle
- Seven unlike SDLC stages are 1) Requirement drove and analysis 2) Feasibility report: three) Blueprint iv) Coding 5) Testing: 6) Installation/Deployment and 7) Maintenance
- Feasibility Written report stage includes everything which should exist designed and developed during the project life wheel
- In the coding stage, developers showtime to build the entire system by writing lawmaking using the chosen programming linguistic communication
- Installation and deployment face begins when the software testing phase is over, and no bugs or errors left in the organization
- Waterfall, Incremental, Active, V model, Spiral, Big Bang are some of the popular SDLC models
Source: https://www.ntaskmanager.com/blog/software-development-life-cycle-sdlc/
0 Response to "Deena Engel the Life Cycle of a Software Based Piece of Art"
Post a Comment